We are living in a time when the number of cars in the world has already exceeded 1.1 billion. It is estimated that it will exceed 2 billion by 2040. Most of these cars have internal combustion engines emitting, among other things, carbon dioxide. In order to improve the air we all breathe, we should shift to emission-free modes of transport whether public or private.
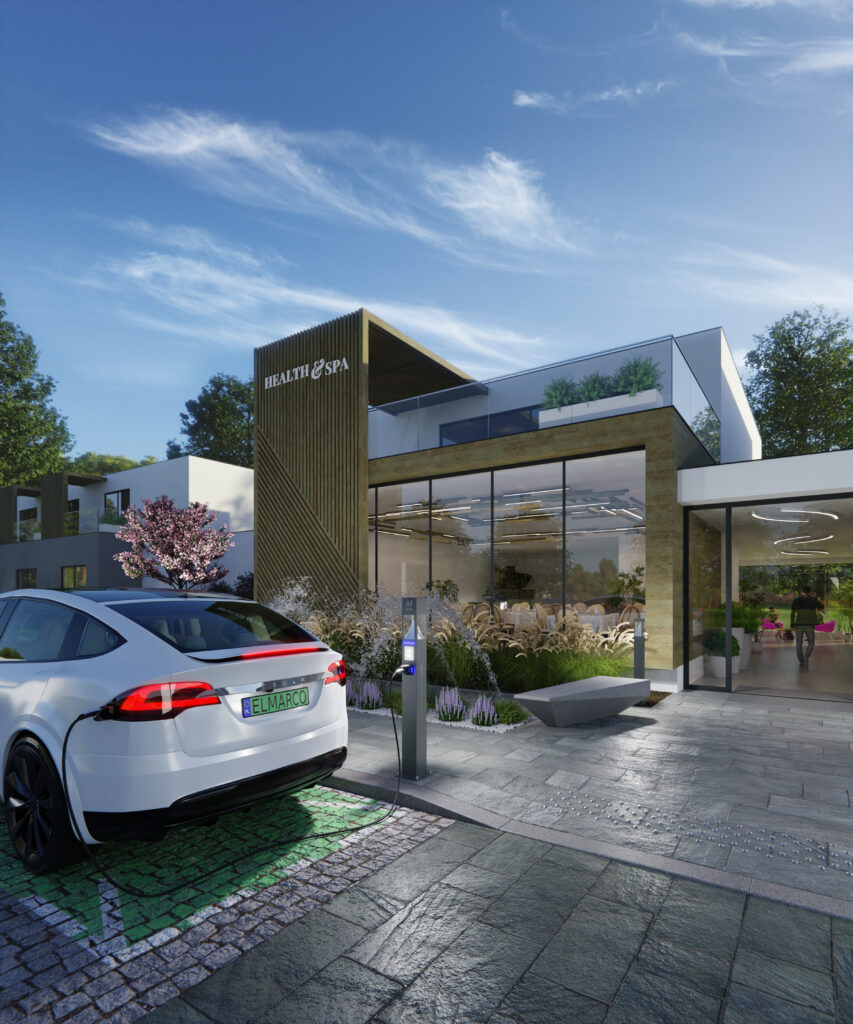
While in large conurbations the use of public transport is a frequent and faster way to get around, outside cities this is more difficult. One solution could be to use electric cars, which are quiet and have no toxic emissions.
As is well known, the purchase of an electric car itself is not a problem in terms of availability. The problem may be the infrastructure (e.g. chargingstations ), of which there are still too few for the convenient use of such vehicles, particularly outside cities. Many solutions can be found on the market that allow charging stations to be installed not only at large shopping centres, but also on private property, at restaurants, hotels, public institutions and other such places in smaller towns. They are also often mounted in lamps, so that there is no need to find additional space and power for them.
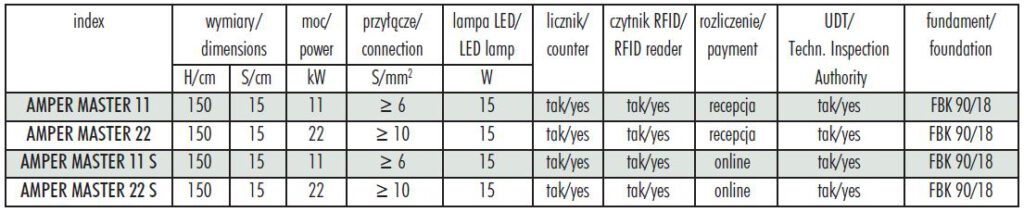
Amper Master Charging Station 22

TECHNICAL DATA:
Aluminium body 150x150x1500mm, IP 54
LED luminaire 10-18W, controlled by a twilight switch
Charging socket: IEC62196 type-2, 32A
Overcurrent protection 32A
Residual current protection 30mA type-A, 6mA DC
Overvoltage protection type-2, 350V/1500V
Energy measurement: MID meter
Network layout: TNC-S, TN-C, TT
Communication: LAN cable, Wi-Fi module, GSM module
Possibility of integration with OCP
communication
protocol: OCPP 1.6J (allows remote switching on and off)
What types of charging stations are there?
There are two main types of AC (alternating current) and DC (direct current) chargers.
- AC charger – charges with alternating current, and this means longer charging times. It uses 230V or 400V. The power of the charger is up to 13 kW when the charger does not have EVSE protection (a controller that ensures the optimum level of charging current so that it does not exceed the insulation strength of the cable). However, when the charger has EVSE protection, the charging power can increase to up to 22 kW.
- DC charger – uses alternating current and converts it into direct current. It uses 400 V – 800 V, the charging power is 50 kW – 350 kW. At charging powers above 100 kW, the cables are cooled with liquid due to the high amount of heat generated. It is also worth noting that fast chargers require a good layout of the power grid and preferably energy storage facilities. In addition, they can cause significant maintenance costs.

What should guide our choice of charging station?
- It is necessary to determine the power we have at the station installation site. Installing a station with too much power in relation to the capacity of the installation can cause overloading of the network.
- The power of the station itself and the charging speed. The charging power needs to be matched to the charger that the electric car is equipped with.
- The type of socket in the car. It is also important that we pay attention to what type of socket our car has (adaptors are available).
- The type of charger, i.e. whether the charger is with a factory cable or just the socket itself. Keep in mind that charging stations with a factory cable will have the option of connecting vehicles with a specific type of plug. Charging stations with a socket will give you the possibility to charge any electric vehicle, you will only need a cable that matches the type of car that is usually on board.
- Charger status: private and public. Private chargers are for home and business use, e.g. employees (no charge). Public chargers give paid access to any user of an electric car. They have energy meters with access to payment by RFID or other payment cards directly from the developer or a third-party operator, such as Elocity. Registering such a station in the EIPA (Alternative Fuels Infrastructure Register) registry gives the possibility of GPS location on maps, as well as booking the service.
- Additional features. It is possible to connect the station to a Wi-fi or GSM network, allowing the station to be managed from a mobile phone.
We should remember that charging stations, even those intended for domestic use, should be fitted by a qualified electrician who will check the installation and fit it correctly. Irresponsible selection of the station for the installation and incorrect installation can have a negative impact not only on our car, but also on the safety of the entire installation to which the charging station is connected.




